Genus/species (aliases): Candida parapsilosis (Blastodendrion globosum. Brettanomyces petrophilum, Monilia parapsilosis, Sacchromyces vossii)
Classification: Ascomycete, anamorph
Morphology:
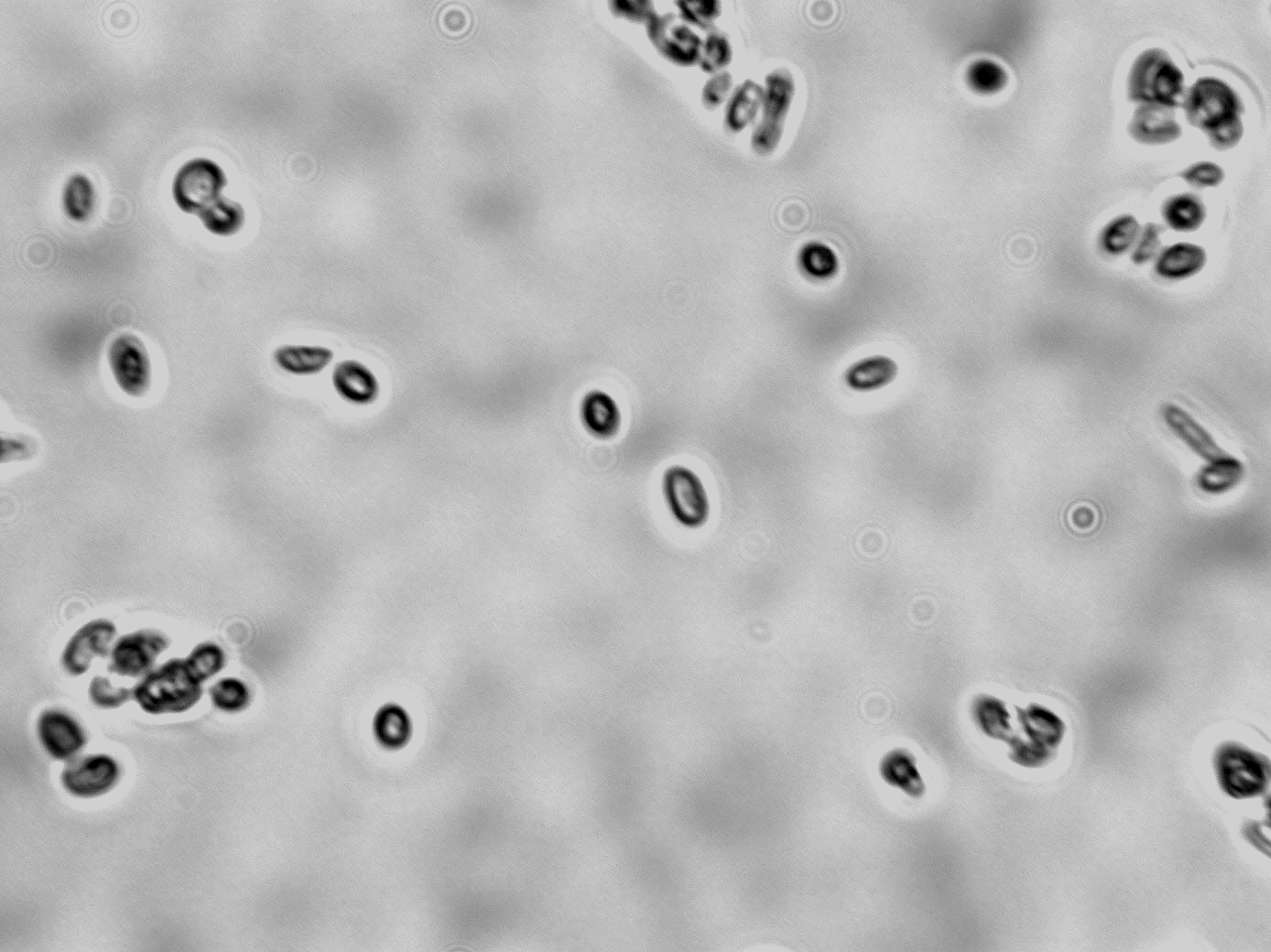
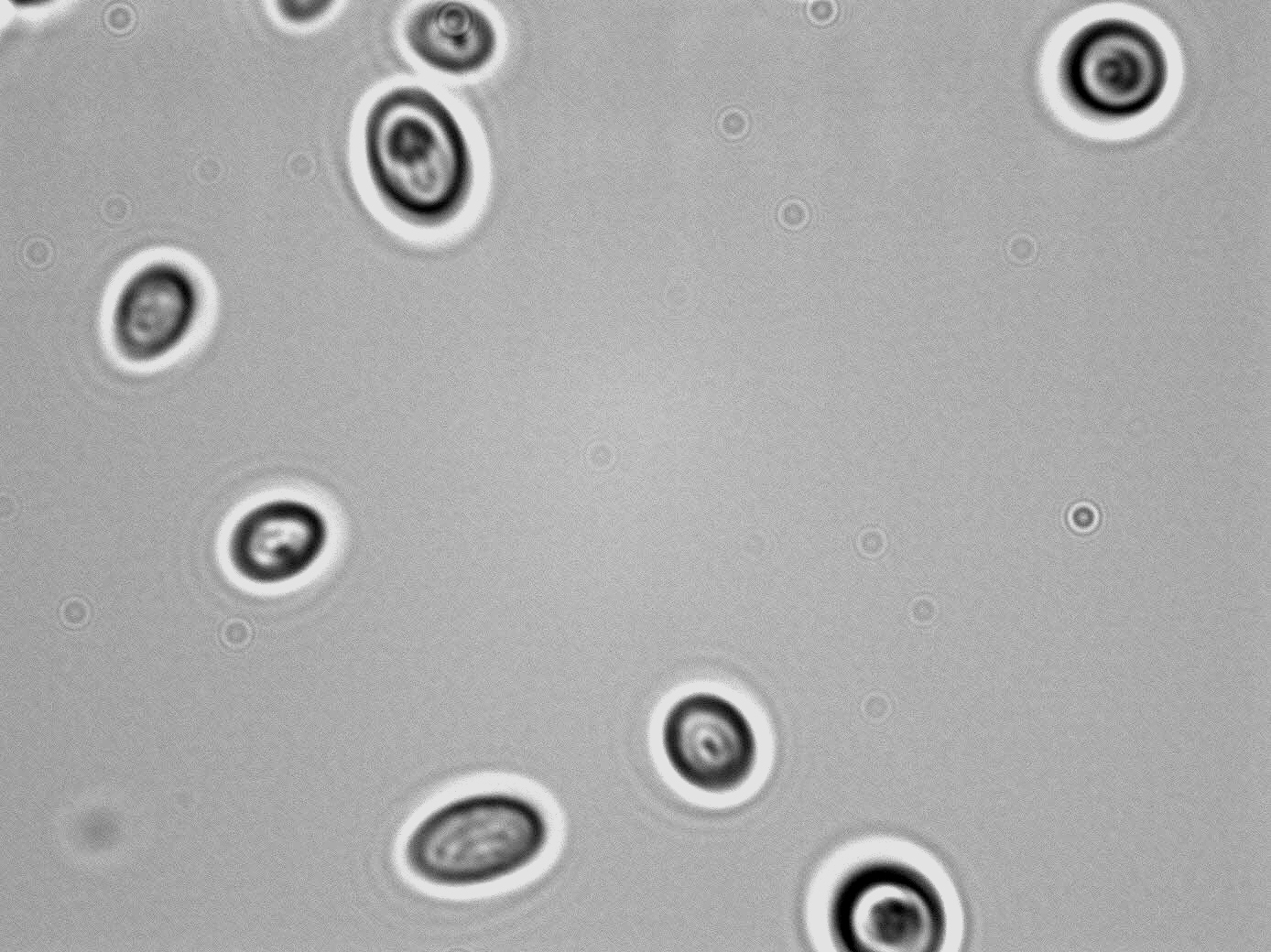
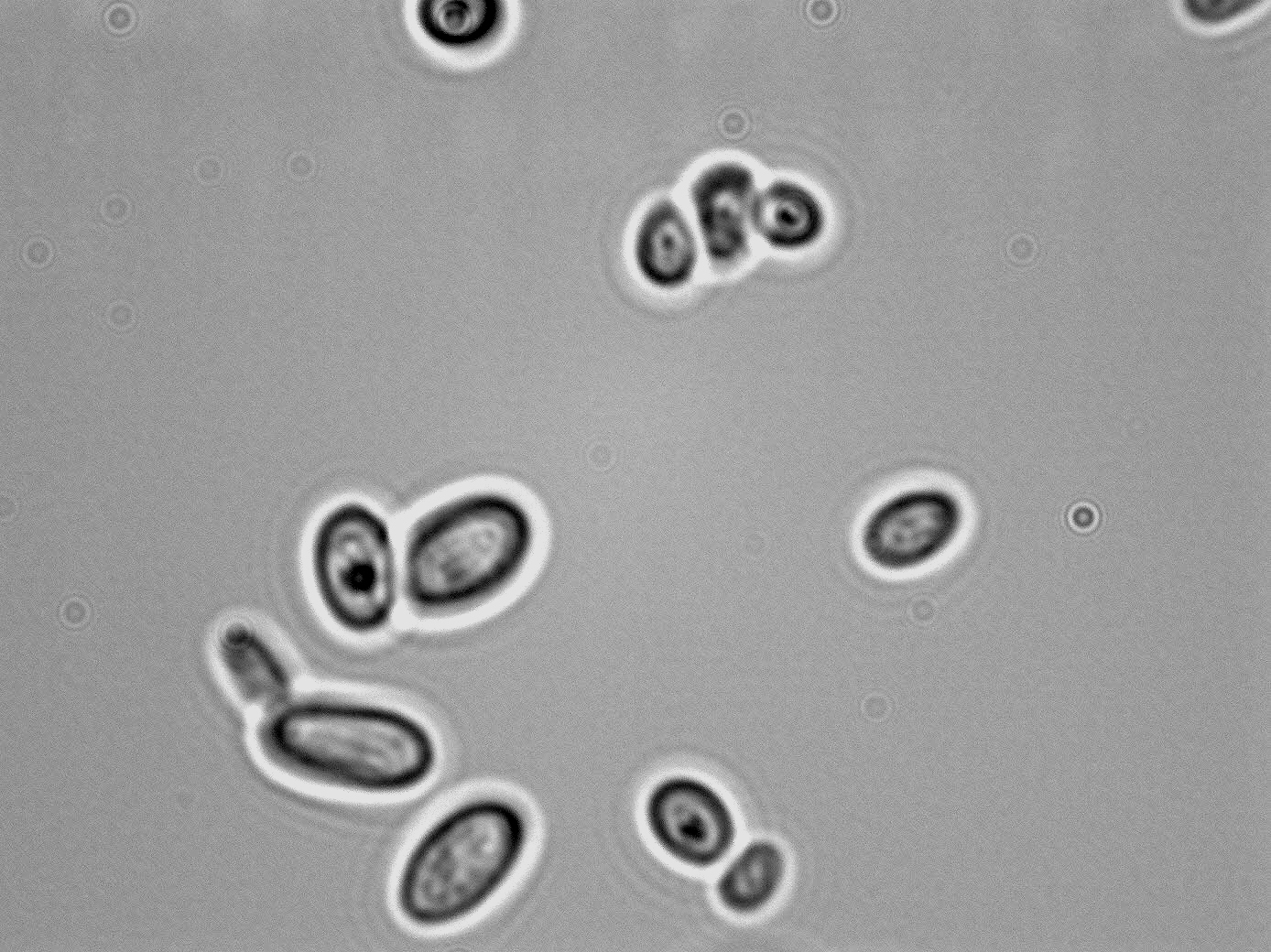
- Cell: reproduces by budding, ovoid, elliptical and elongated occurring singly, in pairs or short chains or cluster; simple to complex pseudohyphae formed
- Colony:
- YPD: cream-colored to yellowish, glossy, soft, smooth, some strains have wrinkled colonies
- Spore: asexual blastopsores formed on pseudomycelia
- Zygote: NA
- Ascus: NA
- Liquid Growth: Biofilm, pellicle, sediments and rings ma form
 |
 |
 |
Physiological Traits:
- Fermentation: Glucose; Galactose variable; Sucrose and Maltose absent or weak fermentation.
- Assimilation: Galactose, Sucrose, D-Xylose, Ribitol, D-Mannitol, Maltose, Trehalose, L-Arabinose, Glycerol, D-Glucitol; growth on Sorbose, D-Ribose, Lactate, Succinate and Citrate is variable. No assimilation of nitrate; Cadaverine used as sole N source; some strains may use ethylamine or lysine as sole N source; no to weak growth in vitamin-free medium: requires biotin
- Growth: 37C: +
- Growth sensitivities: 10% NaCl: +; some strains will grow on 0.01% cycloheximide, no growth at 0.1% cycloheximide
- Chrosmosome bands: 5 to 14
Ecological Traits:
Found on grape surfaces, human skin, soil.
Distinguishing Features:
Can be pathogenic in humans.
Role in wine:
Can be part of natural grape flora. Can ferment to a limited degree.
Sensitivities:
- SO2: X
- Sorbate: X
- DMDC: X
- pH: X
- Acids:
- Ethanol: X
- Anaerobiosis:
- Heat:
